Still struggling with ASC 606 compliance? Maxio can help you maintain compliance and improve the reliability of your accounting records.
Since December 2021, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) has required all companies to adopt ASC 606. This accounting standard changed how businesses recognize revenue, and adoption has been especially challenging for rapidly growing companies that lack the resources to understand and maintain the new standards.
Despite the clear advantages of this requirement for revenue recognition, adhering to ASC 606 is nearly impossible without the right software. To help companies that are still struggling with this standard, Maxio created an advanced workflow specifically designed for ASC 606 revenue recognition.This post outlines what you need to do to maintain ASC 606. Then, it explains how our Advanced Revenue Management Module can prevent this process from becoming a pain in the SaaS.
What is the revenue recognition principle?
Per FASB, the revenue recognition principle establishes the core idea that businesses should “recognize revenue in a manner that depicts the transfer of goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for these goods or services.”
Or, to put it in simpler terms, the revenue recognition principle allows businesses to account for revenue as they earn it over a period of time while fulfilling a contract.
Revenue recognition and ASC 606: SaaS implications
On May 28, 2014, ASC 606 was jointly released by the FASB and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). By changing how businesses recognize revenue, ASC 606 accomplished the following:
- Fostered a more robust framework for addressing revenue issues as they arise
- Standardized financial statements for easier comparisons of companies in different industries
- Required more thorough disclosures, so investors and auditors can understand the rationale behind a company’s metrics
The revenue recognition principle is important to software as a service (SaaS) for a few reasons:
- It helps craft a documented revenue policy the your business
- It ensures businesses follow current FASB guidelines for revenue recognition to produce audit-ready financials
- Investors take into account financial metrics like total GAAP revenue in addition to core SaaS metrics like ARR when evaluating the health of your business
Subscription-based companies have varied ways of recognizing revenue that depend on when their performance obligations have been “satisfied”. Because performance obligations can be met at different times depending on your contract structure, recognizing revenue gets confusing and messy for SaaS companies. But that’s where the revenue recognition principle comes in.
For instance, many software companies experience unbilled revenue (revenue that has been earned) or deferred revenue (also known as unearned revenue, occurring when customers pay upfront for services not yet received, like an annual subscription). ASC 606 provides guidance for properly including both of these revenue types in your monthly recurring revenue (MRR) calculations.
Common methods of revenue recognition
To understand the advantages of ASC 606, you need to understand the different types of revenue recognition.
- Completed Contract Method: You report revenue—and the expenses required to fulfill each contract—when each contract is completed
- Cost Recovery Method: You recognize revenue when you recoup the costs associated with the contract
- Installment Method: Your client makes installment payments, and you recognize profits based on the proportion of the installment to the full value of the contract
- Percentage of Completion Method: While working to complete a contract, you recognize revenue based on the percentage of completion for your project
- Point-in-Time Method: Rather than recognizing revenue over time (based on installment payments, percentage complete, or cost recovery), you recognize revenue when you transfer control of a good or service to the client
- Proportional Performance Method: You recognize revenue based on the portion of the contract you’ve successfully completed or performed
- Sales-Basis Method: You recognize revenue at the point of sale (this is the most straightforward option, but it’s not accurate for most businesses)
When deciding how to approach revenue recognition, you must consider your unique business model. Consider your contract terms and subscription plans. For example, if you offer usage-based subscription plans, you need to recognize revenue differently than a business that sells deliverables like software licenses at a set price point.
No matter which recognition model you choose, just be sure that you adhere to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).or services not yet received, like an annual subscription). ASC 606 provides guidance for properly including both of these revenue types in your monthly recurring revenue (MRR) calculations.
Challenges of revenue recognition
As you know, the price listed on your sales order or contract may not always equal the price used for revenue recognition. This is especially true for B2B SaaS companies with complex, sales-negotiated contracts. Unfortunately, revenue recognition gets messy when you start introducing concepts like:
- Upfront set-up fees
- Variable pricing
- Potential upgrades/downgrades
- Add-on options
- Separate consulting services
- Discounts/credits
- Early termination
Added complexity increases the risk of human error (not to mention the hours spent in tedious, repetitive tasks). The key to maintaining successful compliance and saving your team a ton of time is automation. That’s where Maxio comes in.
Maxio streamlines the complex process of reallocating your total contract price to each performance obligation. With flexible, easy-to-use formulas, Maxio makes calculating stated, standalone selling prices a breeze.
How to record revenue recognition
Following this five-step model is the best way to abide by the revenue recognition principle.
Step 1: Identify the contract(s) with a customer
This standard starts with identifying the contract. The contract must have identifiable rights, clear payment terms, and a commercial substance. Most importantly, it must be approved by all parties involved, and there should be a strong probability that the contract will be carried out.
You should expect to collect the consideration outlined in the contract, and in exchange, the goods or services identified should be transferred to the customer.
Step 2: Identify the performance obligations in the contract
According to the FASB glossary, a performance obligation is a contractual promise to transfer a distinct good/service or a bundle of goods/services. Performance obligations can either be explicit or implicit, and it’s up to you to determine which category a performance obligation fits into.
(For example, if you would reasonably expect a customer to pay for a single promise, even if it were separated from the rest of the contract, you likely have a performance obligation.) Determining what is or isn’t a performance obligation (especially in a way that’s defensible to auditors) can be confusing, so companies often hire outside consultants to help.
Step 3: Determine the transaction price
The transaction price specifically refers to the amount of consideration the company expects to receive in exchange for transferring goods or services. It represents the monetary value assigned to the contract and may be affected by various factors, such as discounts, rebates, refunds, or variable consideration based on performance milestones or contingencies.
In recording revenue recognition, you must have a clearly determined transaction price. This amount could be a fixed or variable, based on time to completion or other performance factors, or a combination of the two. However you determine your transaction price, it must be clearly recorded.
Step 4: Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract
To comply with ASC 606, companies must show they have consistent and controlled methods of reallocating revenue to performance obligations based on their standalone selling price.
This is where adopting a revenue recognition tool like Maxio will really come in handy. Maxio’s revenue recognition module allows you to establish and enforce specific rules (formulas) for re-allocating your total contract price to those performance obligations which can then be automatically (read: consistently) applied to new records.
Leveraging an automated recognition tool also helps you cleanly manage the various recognition methods your company may need to apply to different products or subscription types. For example, in Maxio you can assign specific amounts, carve out a part of one obligation’s price and allocate it to another, or simply use a dynamic formula to perform the needed calculation. Carve-outs come into play when an item is not listed in the contract (explicit performance obligation), but may be buried in the terms and conditions or is a generally accepted business practice provided to your customers (implicit performance obligation).
This can be useful when you sell and list only one subscription on your order, but you’re required to allocate part of that subscription to the ongoing support services provided in the contract.
Step 5: Recognize revenue as the entity satisfies a performance obligation
Once you’ve reallocated the price, you can finally recognize your revenue.
Check out this example of how a SaaS business might create an accurate representation of their financials by recognizing the revenue from one subscription between support, installation, and the service itself.
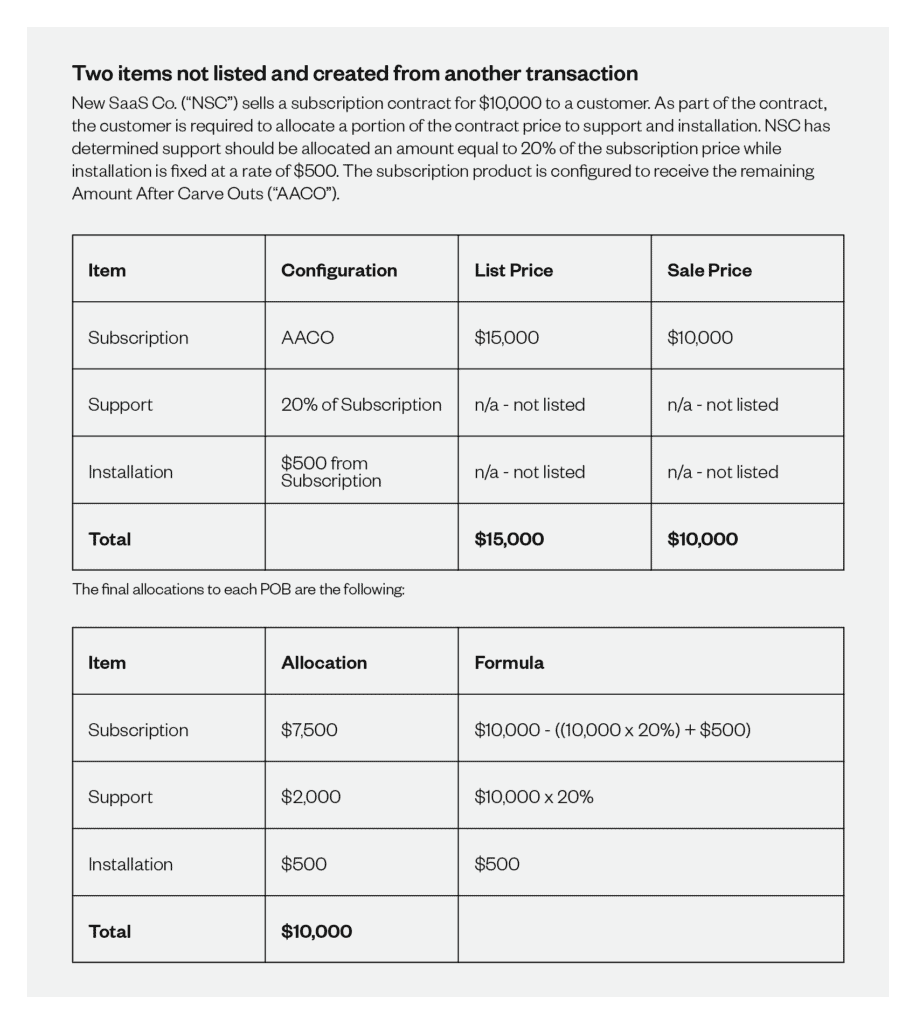
Examples of revenue recognition in SaaS
Revenue recognition: Monthly vs. annual subscriptions
For SaaS companies, monthly and annual subscriptions require distinct approaches to revenue recognition. With monthly subscriptions, revenue is typically recognized incrementally as the service is delivered each month. Annual subscriptions, however, may involve upfront payments, requiring deferred revenue recognition. The company recognizes revenue monthly over the subscription term, ensuring compliance with ASC 606.
Revenue recognition: Subscription upgrades or downgrades
Changes in subscription tiers mid-contract, such as upgrades or downgrades, introduce complexities. For an upgrade, additional revenue is recognized once the performance obligation for the upgraded service is satisfied. Conversely, downgrades may require adjusting recognized revenue and managing customer credits or refunds. Clear policies ensure the accurate allocation of transaction prices in these scenarios.
Revenue recognition: Subscription holds or cancellations
When customers pause or cancel subscriptions, companies must adjust revenue recognition accordingly. For a subscription hold, recognition pauses during the hold period and resumes once the service is reinstated. Cancellations may involve refunds or prorated adjustments, requiring precise allocation of recognized and unearned revenue.
Revenue recognition: One-time fees or add-ons
One-time fees for implementation, training, or other setup services are typically recognized based on the completion of the associated performance obligation. Add-ons, such as additional features or services purchased mid-term, require companies to evaluate whether they constitute separate performance obligations or adjustments to existing ones.
Revenue recognition: Refunds or bad debts
Handling refunds and bad debts involves revisiting previously recognized revenue. For refunds, the company reverses a portion of the recognized revenue, ensuring compliance with contract modifications under ASC 606. Bad debts, meanwhile, require adjustments to receivables and may impact financial reporting metrics like cash flow and profitability.
Maintain ASC 606 compliance with Maxio
Maxio streamlines the complex process of reallocating your total contract price to each performance obligation. With flexible, easy-to-use formulas, Maxio makes calculating stated, standalone selling prices a breeze.
Maxio’s advanced revenue recognition module enables you to migrate from the old (ASC 605) to new (ASC 606) standards and easily maintain compliance moving forward. Take a tour of Maxio, or talk to us about how we can help your business automate your revenue recognition—no matter how complex your business model is.