Here’s a hard pill to swallow: your customers probably aren’t going to stick around forever.
Whether it’s due to budget cuts, competitors creeping in, or simply moving upmarket, eventually your customers will find a reason to say goodbye. That’s why it’s crucial to understand how customer lifetime value (CLTV) impacts your business.
It’s natural for businesses to experience customer churn over time, but taking proactive steps to extend the average customer lifespan can help maximize your revenue and profitability. In this article, we’ll explore the ins and outs of customer lifetime value and the key metrics involved in calculating it. We’ll also discuss how reducing customer churn rates can improve your CLTV and overall business model.
What is Customer Lifetime Value?
Customer lifetime value (CLV) is a metric that calculates the total revenue a business can expect from a single customer over their average customer lifespan. It is sometimes referred to as CLTV, CLV, or LTV across different organizations.
By understanding your CLV, you can educate your go-to-market teams on the average revenue generated by individual business lines and customer segments. Not only is this especially helpful when introducing new products or cross-selling to existing customers but CLV can also be used by early-stage SaaS companies or startups who are still trying to find product-market fit.
Referencing your CLV can also help you identify opportunities to improve the customer journey and life cycle: Is there a certain growth stage or revenue range where customers are churning? Do certain products or features contribute to a higher CLV? What do customers with a higher average CLV have in common?
Overall, CLV provides a comprehensive view of a customer’s value to your business, allowing for strategic decision-making and improved financial outcomes.
Why is Customer Lifetime Value Important?
There are several reasons why CLTV is important for your business. Here’s a quick look at why you should start measuring your customer lifetime value:
Increases Total Revenue: By understanding the CLTV of your customers, you can make strategic decisions about how much you should be willing to spend on customer acquisition. If the CLTV of your customers is high, you could justify a higher customer acquisition cost, knowing that the long-term return on investment will be worth it.
This can result in increased revenue for your business, as you are able to acquire more high-value customers. This is a common scenario in sales-led SaaS companies where annual contract values (ACV) are higher—resulting in greater CAC—and customer contracts typically last several years on average.
Enhances Strategic Decision-Making: Knowing the CLTV of your customers can help you make strategic decisions about how to invest in your business. For example, if you know that the CLTV of your customers is low, you may want to invest more in R&D and determine which product gaps are causing customers to churn. Alternatively, if the CLTV of your customers is high, you may want to invest more in Customer Success to ensure that your customers are satisfied and continue investing in your SaaS.
Informs Customer Segmentation: Calculating the CLTV of your customers can also help you segment your customer base. By identifying your most valuable customers, you can create targeted marketing campaigns and customer loyalty programs to keep these customers coming back. On the other hand, if you identify customers with a low CLTV, you may want to focus on retaining them by offering incentives or promotions to increase their loyalty and repeat purchases.
You can learn more about incentivizing customers who are at high risk for churn in our guide “Scaling During a Recession: Winning Strategies for SaaS Leaders”.
Increases Customer Satisfaction, Loyalty, and Retention: By understanding the CLTV of your customers, you can create strategies to increase customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention. For example, if you identify that your most valuable customers are those who pay for a certain subscription tier or product offering, you may want to:
- Ask them to participate in a case study to share their success with your SaaS
- Tell your go-to-market teams to reach out to them about upsell or cross-sell opportunities
- Advise your CSMs to ensure they have all the resources and support they need to continue investing in your SaaS
Reduces Customer Acquisition Costs: By understanding the average CLTV of your customers, you can determine the maximum amount you should be willing to spend to acquire a new customer, optimizing your go-to-market budgets.
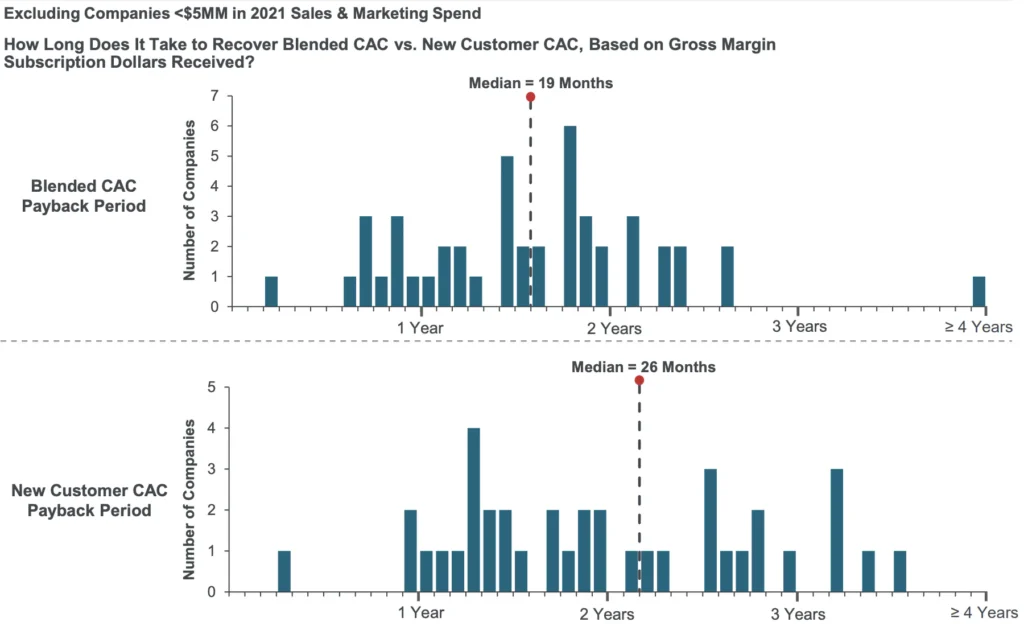
According to KeyBanc’s 2022 Private SaaS Company Report, the average CAC payback period for new and existing customers at SaaS companies is 19 months, and the average CAC payback period for new customers is 26 months—that’s about a 7 months difference in total. This proves that retaining existing customers lead to much better profit margins for SaaS companies.
If the CLTV of your customers is low, you may want to reduce your customer acquisition costs to ensure you’re not spending more to acquire a customer than they are worth.
Essential Customer Lifetime Value Metrics
To calculate CLTV, there are several essential metrics that SaaS owners and operators need to know. These metrics provide insights into the purchasing behavior of your customer base, which can help you make strategic decisions about how to optimize your customer acquisition and retention efforts.
Average Purchase Frequency
While this metric is less relevant for SaaS companies, the average purchase frequency is a metric that measures how often customers make purchases from your business. This metric is essential for calculating CLTV, as it helps you understand how frequently customers are likely to make purchases in the future. By analyzing historical purchase data, you can determine the average purchase frequency of your customer base and use this information to forecast future revenue and CLTV.
Average Purchase Frequency = Total Number of Purchases / Number of Unique Customers
Average Purchase Value
Average purchase value is a metric that measures the average amount that customers spend on each purchase. For sales-led SaaS companies, this metric is typically referred to as the annual contract value (ACV). This metric is important for calculating CLTV because it helps you understand the revenue potential of each customer. By analyzing historical purchase data, you can determine the average purchase value of your customer base and use this information to forecast future revenue and CLTV.
Average Purchase Value = Total Revenue / Total Number of Purchases
Average Customer Value
Average customer value is a metric that measures the average amount of revenue that each customer generates for your business. This metric is important for calculating CLTV because it takes into account both the average purchase frequency and the average purchase value. By analyzing historical purchase data, you can determine the average customer value of your customer base and use this information to forecast future revenue and CLTV.
Average Customer Value = Average Purchase Frequency x Average Purchase Value
Average Customer Lifespan
The average customer lifespan is a metric that measures how long users will continue subscribing or investing in your software. This metric is important for calculating CLTV because it helps you understand how long you can expect each customer to continue generating revenue for your business. By analyzing historical purchase data, you can determine the average customer lifespan of your customer base and use this information to forecast future revenue and CLTV.
Average Customer Lifespan = 1 / Customer Retention Rate
CTLV/CLV Formula
Now that we’ve analyzed the individual metrics that make up your CLTV, let’s break down the formula used to calculate it.
The CLTV formula calculates the total value of a customer over a period of time. It is the sum of the gross margin generated by the customer during that period, minus the cost of acquiring and servicing the customer.
The formula is simple: CLTV = Customer Value x Average Customer Lifespan.
To calculate CLTV, you first need to know the value of each customer. This value is determined by the customer’s behavior, such as the number of purchases made and the average purchase value. Once you’ve determined the customer value, you can then multiply it by the average customer lifespan to determine the CLTV.
This formula is a valuable tool for businesses looking to understand the value of their customers over time. By calculating CLTV, businesses can identify their most valuable customers and allocate resources to retain them. It can also help businesses determine the maximum amount they should be willing to spend on customer acquisition, ensuring that they are investing their resources in the most effective way.
Here is a step-by-step overview of how to calculate CLTV using the formula provided:
- Determine the average customer lifespan: This is the average amount of time a customer continues to generate revenue for your business.
- Determine the average purchase value: This is the average amount of money a customer spends on each purchase.
- Determine the number of purchases: This is the number of times a customer makes a purchase during their lifetime with your business.
- Calculate the customer value: Multiply the average purchase value by the number of purchases.
- Calculate the CLTV: Multiply the customer value by the average customer lifespan.
By using this formula to calculate CLTV, you’ll gain valuable insights into the value of your customers over time so you can make strategic decisions about how to allocate resources to retain your most valuable customers.
Example CLTV calculations
Calculating CLTV is an important metric for SaaS businesses to truly understand the lifetime value of their customers. Here are two fictional examples demonstrating how SaaS owners and operators can determine CLTV on their own:
Example 1:
A SaaS company wants to calculate the CLTV of its current customers. They have determined that the average customer lifetime is four years, and the average revenue per user (ARPU) is $120 per month. They also know that the customer acquisition cost (CAC) is $800.
To calculate CLTV, they can use the following formula:
Customer Value = ARPU x Average Customer Lifespan
Customer Value = $120 x 48 months = $5,760
CLTV = Customer Value – CAC
CLTV = $5,760 – $800 = $4,960
This means that the lifetime value of a customer is $4,960—this information can then be used to make strategic decisions about customer retention and acquisition.
Example 2:
A SaaS company wants to calculate the CLTV of its customers using a predictive model. They have determined that the important metrics for their business are the average order value (AOV), the average purchase frequency, and the average customer lifetime. They have gathered data over the past three years and determined that the AOV is $200, the average purchase frequency is six times per year, and the average customer lifetime is three years.
To calculate CLTV, they can use the following formula:
Customer Value = Average Purchase Value x Average Purchase Frequency
Customer Value = $200 x 6 = $1,200
CLTV = Customer Value x Average Customer Lifetime
CLTV = $1,200 x 36 months = $43,200
This means that the lifetime value of a customer is $43,200.
Using CLTV to inform your financial operations
Understanding customer lifetime value is critical for the success of any business—but for SaaS companies, the importance of CLTV is even more pronounced.
Since SaaS businesses rely heavily on recurring revenue from existing customers, understanding the lifetime value of each customer is crucial to their success. By using the CLTV calculation, SaaS companies can identify which customers are most valuable, which customer segments to focus on, and how to optimize pricing and marketing strategies.
Need help drilling down into your CLTV and other critical SaaS metrics? Maxio’s drillable SaaS metrics reports help SaaS companies take the guesswork out of growth so they can confidently prep for audits, board meetings, or funding rounds.
See how other SaaS companies are using Maxio to dig into their SaaS metrics.